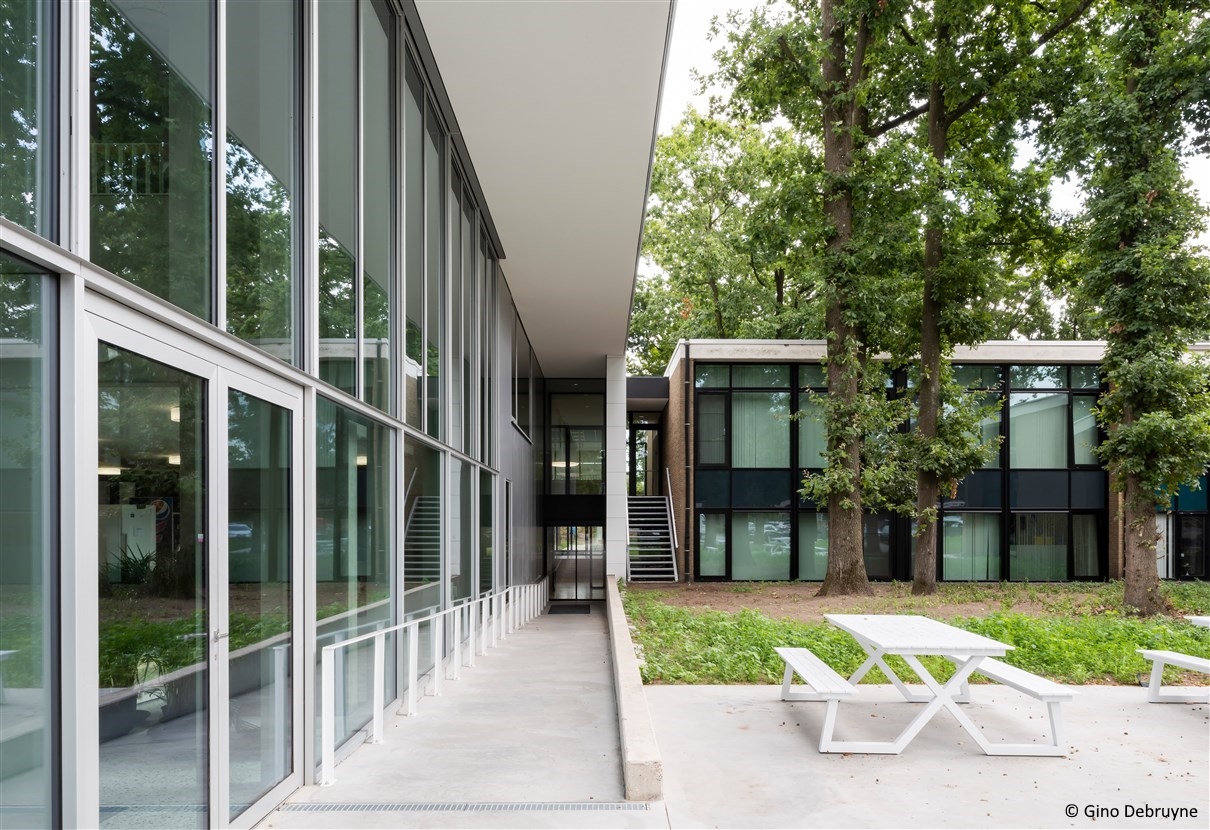
Syntra West reception building
Brugge, Belgium, Europe
| Total technical installations cost: | € 448.818,99 VAT excluded |
| K Level / Energy class : | 30 (K level) |
| E Level: | 53 (E level) |
Project description:
Syntra West’s infrastructure in Bruges was expanded by connecting two existing buildings to each other.
The new cafeteria, seven classrooms and a reception desk are housed in this new volume.
Educational buildings are designed from the point of view to have a long lifespan and low operating and maintenance costs. Another determining factor is the varying occupancy rate of the building depending on the time of the day and the year. Based on this, various sustainable techniques were applied; the cafeteria can be acclimatized separately from the classrooms to limit the fan consumption, absence detection is used for the lighting in the classrooms, … The boiler and technical room were provided in a separate room on the roof and additional solar panels were installed. The advantages of a technical room on the roof are the provision of fresh air, exhaust air and chimney towards the environment, which ensures a cost-efficient design.
A healthy and comfortable working and learning environment has a major impact on the productivity of the users. For example, the occupied spaces must be sufficiently heated or cooled without creating an audible draft. Natural and artificial ambient light must be pleasant for the eyes, the room must not be light or too dark. For this purpose, sensors were used that measure daylight in order to adjust the amount of artificial light.